Papilloma is a benign formation on the skin or mucosa caused by one of the many types of viruses in the Papovaviridae family. The human papilloma virus, or HPV, is the generic name for a group of non-wrapped DNA viruses that are transmitted in different ways. HPV infection can occur during sexual intercourse, with microtrauma of the mucous membranes and skin, during childbirth (from an infected mother to a child).
Human papilloma virus in adults
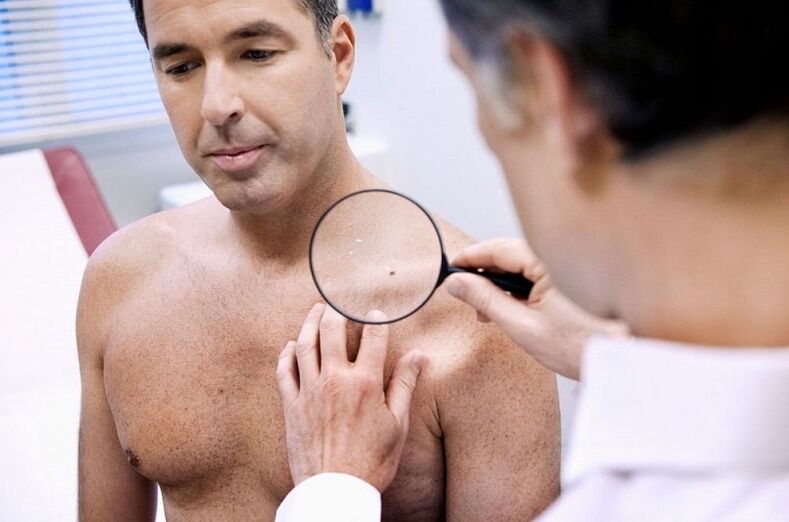
Human papillomavirus (PVI) infection is quite common. Numerous studies show that over 80% of the young population are carriers of it. The infection, entering the body, affects the squamous epithelium of the skin and can multiply in it for years. Its various types, which affect the mucosa, cause the appearance of benign formations of the conjunctiva, mouth and genitals.
Papillomas in women
Human papillomavirus infection is equally threatening to men and women. But some types of pathogenic microorganisms pose a great risk to the health and life of women. Numerous studies have shown that HPV can cause cervical cancer.
Papilloma virus in pregnant women
A sharp weakening of the immune system and hormonal imbalance can provoke active reproduction and symptomatic manifestations of the papilloma virus, which has been inactive in the body for a long time. During pregnancy, the appearance of papillomas on the skin and mucous membranes can frighten expectant mothers. In this case, the woman needs an urgent consultation with a gynecologist.
HPV is not a contraindication to conception, although at birth there is a high probability of infecting the baby.
Papillomas in men
Papilloma in men for the most part does not give clinical manifestations. But men are at the same time a source of infection and infect their sexual partners. In the normal state of the immune system, the activity of pathogenic microorganisms is reduced to zero. But with a lack of immunity, the situation can change and the presence of the papilloma virus in the blood will begin to appear actively and in some cases aggressively.
The type of sexually transmitted infection that causes genital warts affects both men and women. HPV 16 and 18, which can cause cervical cancer in women, are rarely found in men. Once in the body, the papilloma virus of this type stays in the urethral canal for some time, after which it eliminates itself due to the lack of a favorable environment for its reproduction. Genital warts in men can appear:
- most often in the coronary groove and frenulum of the penis;
- much less frequently on the body of the penis or on the head;
- in the area of the external opening of the urethra;
- in the urethra itself;
- in the perianal region and in the anal canal.
Compared to women, papilloma in men rarely causes the development of cancer. Diagnosing HPV in the male body is also difficult.
Human papilloma in children
Papillomas in women and men, as well as in children, affect all organs with integrative or transient epithelium. It can be the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx, respiratory tract. Human papillomavirus transmission in childhood occurs:
- during the intrauterine period of fetal development;
- when the baby passes through the birth canal of the mother;
- the way of contact-home from parents to baby;
- within the team (kindergartens, schools, sports and development sectors).
But even if a child is infected, the papilloma virus from the body can eliminate itself after a certain period of time. If this does not happen immediately, after the onset of puberty, in many cases, papillomas in the body and mucous membranes disappear.
Papilloma in the body
The most common in children are clinical manifestations of human papilloma in the form of common or vulgar warts. They are usually located on the inside and back of the palms or in the knee area. But often the appearance of papillomas with a prominent keratinized surface on any part of the body. They cause no discomfort and are painless. With injuries, such formations can begin to hurt and bleed.
Papillomas in children in the laryngeal mucosa

The most common diagnosis in children, if the human papillomavirus is present in their body, is laryngeal papillomatosis. If the infection occurs during birth and the infection is transmitted from mother to child, its external manifestations are usually observed before the child reaches the age of five. The cause of laryngeal papilloma is the penetration of HPV types 6 and 11 into the body of the child.
Ways of infection, types of PVI and their manifestations
The papilloma virus is highly contagious. The ways of its transmission are different, which significantly expands the number of people at risk. More than a hundred species of papilloma pathogens are divided by modern medicine into different types, characterized by their routes of transmission, external manifestations and the level of damage to health.
How human papilloma is transmitted
Papillomavirus infection can occur through sexual intercourse, through home use or during childbirth, in which pathogenic microorganisms are transmitted from mother to child. It is also possible for a person to self-infect with one of the papilloma viruses. Autoinoculation can occur with mechanical damage to the skin or mucous membranes, for example, during epilation.
Papillomas: causes of infection through sexual intercourse
For papillomavirus infection, the reasons may be different. But one of the most common is sexual transmission. Moreover, you can be infected not only with vaginal sex, but also with anal and even oral. There are about 40 types of papilloma virus, the reasons for the transmission of which are frequent changes of partners and early onset of sexual activity.
Home transmission of the virus
The secret of HPV is that there is a high probability of its transmission in the family. Several factors can increase the risk of contracting the papilloma virus, the reasons for this are different, for example:
- the presence of cuts and scratches on the skin, as well as excessive dryness of the integrum with the appearance of cracks;
- diseases that weaken the immune system (HIV infection, flu, herpes);
- long-term use of strong-acting drugs that suppress the function of the immune system.
Infection of infants during birth
Like many genital infections, the papilloma virus can be passed from mother to child at birth. Also, the baby can become infected during the prenatal period. If a pregnant woman is a carrier of HPV type 6, 11, 16 or 18, the pathogens most often affect the baby’s oral mucosa. These types of papilloma infections often cause the development of juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis.
Many women mistakenly believe that having a caesarean section will help keep the baby from becoming infected. But even in this case, the chances of transmitting the papilloma virus still remain, and pathogenic microorganisms can be transmitted through the placenta.
How does the human papilloma virus appear?

HPV is a group of viruses that provoke the development of benign tumors in vivo, and under several factors that lead to their malignancy. Depending on the location, the papillomas may be cutaneous or genital. Such neoplasms may appear:
- Common warts are characterized by a dense, rough surface and extra growth. The size of such neoplasms is from 1 mm. As a rule, their appearance is observed on the palms and fingers, in the knee area (mainly in children), but such papillomas may also be present in the body. The spread of common warts is facilitated by a rapid decline in immunity.
- Plantar warts that cause particular discomfort and pain. The causative agents of such neoplasms are several types of HPV: 1, 2, and 4. Apparently, plantar formations can be confused with common calluses. Their size at first is small. But later the papilloma grows, and additional growths may appear around it.
- Flat warts that appear in the presence of HPV types 3 and 10. Such neoplasms practically merge with the skin, can have a round or polygonal shape. Often their appearance is accompanied by itching, redness and soreness.
- Filamentous formations characteristic of virus carriers who have reached the age of fifty years or more. Such papillomas can appear on the eyelid, body, armpit, etc. Their length sometimes reaches 6 mm.
- Genital warts that develop against the background of HPV 6 and 11. In women, such neoplasms can be localized in the anus and rectal mucosa, in the walls of the vagina, in the uterus and vulva, in the groin area.
Types of papillomas
The main risk of papilloma virus in men and women is that in modern medicine it is considered a carcinogenic agent. About a third of its more than a hundred existing varieties affect the male and female genitals and cause the development of genital warts.
Cancer risk classification
An uncoated DNA virus can not only provoke uncontrolled division of skin cells and mucous membranes, but also contribute to the malignancy of neoplasms. However, not every papilloma leads to the development of cancer. Various factors can increase the likelihood of developing oncogenic diseases:
- early onset of sexual activity, frequent change of partners, and preference for anal sex;
- the presence of sexually transmitted infections affecting the genitals, both women and men;
- smoking and alcohol abuse, which negatively affects the state of the immune system and stimulates the appearance of papillomas in an intimate place and other parts of the body;
- use of an intrauterine device as a contraceptive, as well as long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- endometriosis and other diseases of the organs of the female reproductive system.
To determine the type of papillomavirus will help to carry out a thorough diagnosis, the need for which is determined by the doctor.
Non-oncogenic types of viruses
Among the great variety of HPV, there is a group of pathogenic microorganisms that do not pose a particular health risk. Non-oncogenic HPV types include papilloma viruses of genotypes 1, 2, 3 and 5. Their presence in the body causes the appearance of different types of warts on the skin.
- Common and flat warts on the hands and soles of the feet appear when infected with HPV genotype 1.
- Genotype 2 virus leads to the appearance of flat and vulgar formations on the hands.
- HPV 3 causes uncontrolled division of skin cells and the formation of flat warts and juveniles.
Low oncogenic risk viruses
Low-risk oncogenic human papillomas develop when HPV 6, 11, 42, 43 and 44 enter the body. The most common viruses are genotypes 6 and 11. They account for about 90% of all infections. These types of pathogenic microorganisms cause the formation of a special type of genital papillomas - genital warts. Their location in the mucosa of the cervix or penis in men has a certain risk of malignancy of the formations.
High oncogenic risk Papilloma virus
HPV genotypes 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66 and 68 have a high oncogenic risk. More than 70% of infections are infections with viruses of types 16 and 18. Papilloma type 18 is often found in the diagnosis of adenocarcinoma. Pathogenic microorganisms of these species provoke the development of cancer of the cervix, anus, vagina, vulva or male penis.
Classification of the virus by localization of manifestations
The external manifestation of papillomas in women and men can be observed on the skin of open areas of the body, on the soles of the feet, as well as on the skin and mucous membranes of the intimate area. Lesions can be local, and in people with severe immunodeficiency, multiple foci of neoplasms are more often observed. After the virus enters the body, three stages of its development can be marked:
- in the latent phase, clinical manifestations of infection are not observed;
- with a subclinical form, morphological symptoms and signs are minimal;
- clinical stage implies the appearance of papillomas, dysplasia and malignant neoplasms.
The characteristics of the external manifestations depend on the type of virus that has infected the patient's body.
Papilloma in the neck
Papillomas in the neck of carriers of the virus can appear throughout their lives. Such formations are benign, and only offer a person psychological distress. Also, small neoplasms on a thin leg can seize clothes, injure, cause pain, and bleed. If such problems arise, it is advisable to remove the papillomas on the neck.
Papilloma in an intimate place
Papilloma in an intimate place is called genital warts. It can be localized in women in the vaginal mucosa or cervix, in men - in the penis. Also, genital warts can develop in the tissues of the anus. All types of papilloma viruses that infect the genitals can be divided into:
- viruses with a high level of oncogenicity (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35), which significantly increase the risk of malignancy of neoplasms, but do not cause genital warts;
- papilloma virus with a low level of oncogenicity (HPV 6, 11), which causes the formation of genital warts.
Papillomas on the eyelid
Eyelid papillomas are more common in mature people who are carriers of HPV infection. They are usually located on the edge of the lower eyelid. Neoplasms can be in the form of cauliflower. The danger of such formations lies in their constant exposure to direct UV rays and the habit of rubbing the eyes with dirty hands. In the latter case, the risk of infection with papillomas on the eyelid increases significantly. The color of the neoplasm may be fleshy or dark.
Papillomas: treatment and diagnosis
Once introduced into the body, the papilloma virus can behave in different ways. The body's response depends on the type of virus itself, the state of immunity, the presence of concomitant diseases, and other factors that are determined individually for each patient. So, there are three main types of papilloma virus behavior in the human body:
- Pathogenic microorganisms enter the bloodstream and behave passively. In this case, a person is a carrier of the virus and can infect people who are in close contact with it.
- The virus enters the body but does not integrate into cell chromosomes, but at the same time stimulates the uncontrolled division of skin cells and mucous membranes and the formation of papillomas and warts.
- HPV penetrates cells, changing their structure and causing the formation of malignant tumors.
In each case, specific diagnostic and treatment methods are required to identify the virus.
Diagnosis of human papillomavirus
The main type of diagnosis is an external examination of the patient. Relatively important if the infection is manifested by the formation of papillomas (genital warts) in the external genitalia. To determine the presence of HPV in the laboratory and its type of help:
- PCR method. Such a test is very sensitive to detecting an infection that is in a subclinical or latent stage of development.
- Testi i digene. Hybridization analysis revealing 13 types of virus with high oncogenic potential and 5 with low oncogenic potential. As a rule, for a more accurate diagnosis of papilloma virus, the digene test is combined with cytological studies.
In men, the diagnosis of papilloma virus is particularly difficult. Screening for male patients is not important. In this case, diagnosis is possible only in the presence of external clinical manifestations of the disease.
Papillomas: how to get rid of external manifestations
If a person has papillomas on the body, the doctor will tell you how to get rid of them. Trying to cope with the external manifestations itself is not worth it, because it is fraught with dangerous consequences for health, especially infection. Removal of papillomas is necessary for several reasons, namely:
- some types of papillomas can grow and become malignant over time;
- the presence of neoplasms brings psychological distress to the patient;
- papillomas on the body and in the intimate area can be injured and bleed.
But despite this, only a doctor can determine the need to remove papillomas. To do this, you should contact a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist.
Laser papilloma removal

The laser method of papilloma removal is very effective. Its use allows you to quickly get rid of benign neoplasms. Laser cutting of formations with a diameter of about 5 mm takes only a few minutes. However, in some cases it may be necessary to remove the papilloma in several stages. The procedure is performed using local anesthesia. Tissues removed by laser incision are not suitable for histology.
How to remove papillomas by radio wave method
Removing radio waves is an absolutely painless and quick way to get rid of papilloma. During the procedure, the neoplasm rests in the area of its base. After removal, a small dark crust remains in place. The cut material is suitable for histological analysis. When deciding how to remove papillomas without the risk of scarring, the radio wave method is the best option for patients.
Removal of papillomas with liquid nitrogen
Speaking of the external manifestations of papillomas and methods of getting rid of them, one can not fail to mention the removal with liquid nitrogen, otherwise called cryodestruction. This method of removing papillomas in the body is quite effective, but the likelihood of recurrence of external manifestations remains. When you perform the procedure, low-temperature nitrogen affects the papilloma cells, freezing them. This method is characterized by minimal trauma and lack of painful sensations.
Electrocoagulation
Electrocoagulation - the removal of papillomas in the body by means of a targeted effect on neoplasm tissues with a current discharge. This method is very efficient (80-95%). Its main advantage is that after removing the formation from the papilloma, no trace remains. Within a week, only a small crust remains on the skin, which disappears after the period expires. You can not tear it yourself.
Medication treatment

Laser papilloma removal or any other method recommended by a doctor are just a solution to external problems that cause aesthetic, psychological or physical concerns. Neoplasm removal methods have nothing to do with the fight against papilloma virus, the treatment of which requires an integrated approach.
Today, there is no specific medicine for the effective elimination of the papilloma virus from the body and the treatment of its external manifestations. The comprehensive approach to treatment practiced by medicine today is:
- laser papilloma removal, liquid nitrogen and other methods of cutting benign neoplasms;
- immunological therapy aimed at activating the body's natural protective functions;
- general strengthening of the body, taking vitamin complexes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
By contacting a doctor and going through all the necessary studies, you can confirm or deny the presence of the papilloma virus in the body, learn how to get rid of neoplasms and reduce the risk of their recurrence.
HPV and immunity
Once in the body, HPV may not show up for a long time. Papillomas on the eyelid, neck, body or intimate area, which are external expressions of virus activity, appear with a sharp decline in immunity. So, the risk of papillomas on the neck, skin and mucous membranes throughout the body increases significantly with:
- transfer of infectious diseases or surgical interventions;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- persistent stress, hypothermia and other factors that negatively affect immunity;
- long-term use of certain medications;
- the presence of genital tract infections.
Any factor that weakens the immune system can contribute to the multiplication of the virus in the blood. Therefore, it is important to know not only how to remove papillomas, but also how to strengthen the immune system, preventing their recurrence.
Papillomas: alternative treatment
If a papilloma appears on your body, it is strictly forbidden to remove it yourself at home. For a safe and effective treatment, you should see a doctor. The specialist will describe the necessary studies and, based on their results, develop a treatment regimen. Under this scheme, under the supervision of a doctor, the patient can treat the papilloma virus at home.
Prevention of HPV
Preventing the papilloma virus by popular and traditional methods is reducing the risk of infection. There is also the prevention of the multiplication of the virus in the body and the formation in the skin and mucous membranes of such external manifestations as papillomas in an intimate place, in the neck, eyelids, palms, soles of the feet, etc.
Prevention of human papillomavirus infection
So one day you do not have to face the question of how to remove papillomas, you need to remember the main measures to prevent infection with the virus. In intimate relationships with new sexual partners, the use of condoms and other contraceptives, unfortunately, does not protect the body from HPV. Only maintaining a monogamous relationship with a trusted partner can help reduce the risk of infection.
To prevent papilloma virus infection, traditional methods are not as effective as traditional ones. Modern scientists have developed several vaccines that significantly reduce the risk of contracting HPV varieties with high oncogenic potential (6, 11, 16 and 18).
The most suitable age for vaccination is between 10 and 25 years old. Its effect is estimated for approximately 6. 5 years.
Prevention of manifestations of HPV

To prevent papilloma virus activity, alternative treatment is effective with its prescriptions to strengthen the immune system. But before using them, a consultation with a doctor is required. Also, do not forget about such the most effective and safe methods of increasing the body's natural protective functions through sports, healthy eating, strengthening.
Papilloma virus prevention at home is available to everyone. Taking care of your health, remember to visit your doctor regularly for preventive purposes and strengthen your immunity.























